Listening before time runs out
Memories of World War II veterans demonstrate the importance of oral history, Zhao Xu reports.
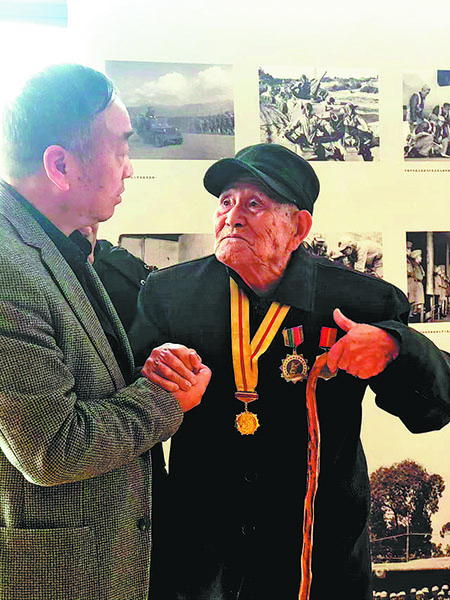


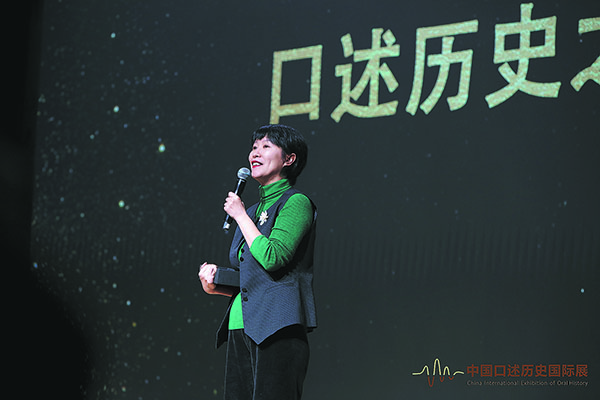
Lin Hui, who heads the Center for Oral History at the Beijing-based Communication University of China, says her entry into oral history happened unknowingly — through a World War II veteran who had fought the Japanese.
"He was in his late 80s. That first day, he narrated his life from enlistment onward, battle by battle, for two full hours," she recalls. "When I went back the next day, he started over from the beginning — and continued to do so each time. It felt as though his memories had to be accessed sequentially."
Lin found herself hearing the same stories on repeat. At times, she tried to gently nudge the veteran past sections he had already covered, hoping to help him move ahead. But she never cut him off.
"Listening lies at the heart of oral history — it is a profound intellectual and emotional journey to which the interviewer must fully commit," says Lin, 43, who at the time was working in television. "Unlike the scientists, cultural figures, and other luminaries I had previously interviewed, these veterans were unsung heroes, whose ordinary lives held extraordinary stories."
That was in 2011, a year before Lin joined the newly established Center for Oral History at the Communication University of China, where she and her colleagues have spent the past 15 years, "racing against time to preserve voices that might otherwise vanish, through means that are deceptively simple: listening attentively, asking questions, and recording", as she puts it.

While Columbia University's Oral History Research Office, founded in 1948, represents the earliest organized effort in capturing oral history in the United States, Lin notes that the institutionalization of the method in China owes much to Premier Zhou Enlai (1898-1976). In 1959, Zhou met with some senior political figures over the age of 60, urging them to record their firsthand experiences for posterity. This initiative led to the creation of a historical materials research committee, which systematically collected and preserved older members' recollections, laying the foundation for China's early oral history practice.
"The only regret is that their stories were preserved in writing rather than captured on tape, whereas oral history in its modern sense typically requires at least a primary audio recording," Lin says, emphasizing the distinction between humanity's long tradition of storytelling and oral history as a scholarly field.
"Another turning point came in 2004, when China Central Television aired a six-episode documentary about Deng Xiaoping, the statesman who guided China through the sweeping changes of the 'reform and opening-up'," Lin says. "By drawing extensively on interviews with people who had known or worked with Deng, the film introduced oral history techniques to a broader audience and became an early catalyst for the method's popularization in China."