Scientists discover new 'cold vent' on ocean floor
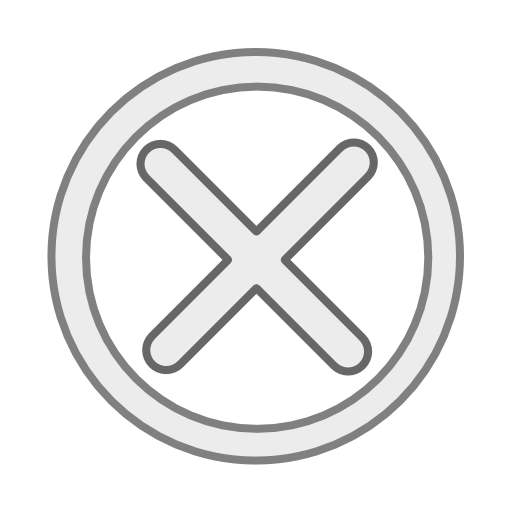


Chinese scientists discovered an active "cold vent" in the South China Sea during a research voyage that concluded on Thursday.
Cold vents are areas where methane, hydrogen sulfide and other hydrocarbons seep out off the ocean floor, providing a unique environment for organisms or the development of topographic features.
Samples and data of organisms, water, gas and sediments were collected to further the study of the evolution and mechanisms of cold vents, according to the China Geological Survey of the Ministry of Natural Resources.
Among the organisms seen was a type of tubeworm-paraescarpia echinospica-in the cold vent 1,390 meters below sea level.
With a 250-year life span, the species is one of the longest living, said Gong Yuehua, a senior engineer of the Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, according to a report by China Central Television.
- Ride like locals: Expats embrace Shanghai's bike-friendly vibe
- China unveils rules for 11th round of natl centralized drug procurement
- Artist, Arc'teryx apologize for fireworks display controversy
- Yellow River maintains good water quality for 3 consecutive years
- Chinese team designs tiny robot sensor for tasks inside bodies
- Chinese researchers develop movable electrode for more advanced brain-computer interfaces