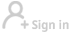The great thaw

 |
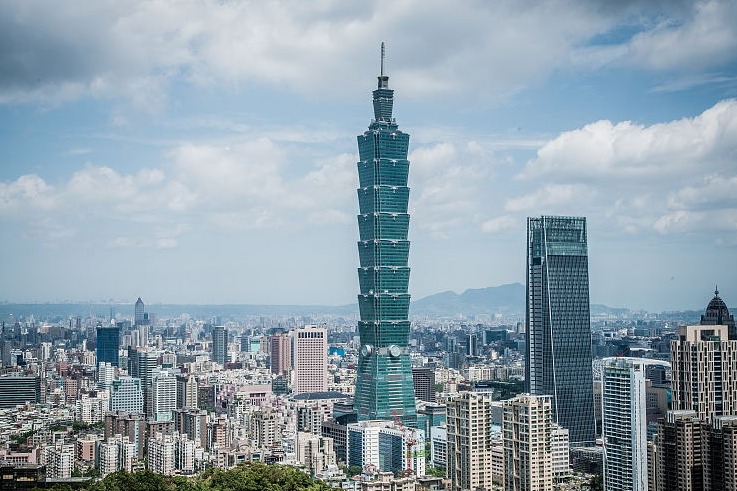
| Mingyong glacier, located on a subsidiary peak of the Meili Snow Mountain in Yunnan province, in October 2009.[Photo by Xu Dong/For China Daily] |
The rates of pullback and contraction, among other changes over 50 years, have varied from glacier to glacier. And, while within the world scientific community, there could be different opinions on the health of glaciers, measured largely by satellite data or on-site monitoring, there is little disagreement over the reason that has triggered the great thaw.
"Glaciers have experienced a universal retreat since the mid-19th century," Liu says. "But the acceleration in shrinkage has become more apparent in recent times."
Climate change, which is commonly known as global warming, is caused by man-made and natural activities, and glaciers are sensitive to it.
The Industrial Revolution (1760 onward) has contributed substantially to climate change.
According to a paper by the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, an affiliate of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the central body in Beijing, glacial retreat in China has been noticed more among small mountain glaciers in the southwest of the Tibet autonomous region, where the mass deficit has been building up since the 1970s.
- Global engineering congress to be held in Shanghai
- 'Lingka' custom in Xizang evolves into new form of cultural tourism, vibrant lifestyle
- From logging to guardianship: How China protects green source of its 'mother river'
- China rescues 10 Myanmar seafarers in South China Sea
- Qingdao sees surge in travelers to S Korea under its temporary visa-free policy
- China's 2025 box office surpasses 2024's full-year gross